

- #Sap ecc stand for software#
- #Sap ecc stand for windows#
#Sap ecc stand for software#
The newer SAP ERP software differs from R/3 mainly because it is based on SAP NetWeaver: core components can be implemented in ABAP and in Java and new functional areas are mostly no longer created as part of the previous ERP system, with closely interconnected constituents, but as self-contained components or even systems. SAP allows the IT supported processing of a multitude of tasks which occur in a typical company. SAP based the architecture of R/3 on a three-tier client/server structure:
In these situations, SAP produced specialized modules (referred to as IS or Industry Specific) geared toward a particular market segment, such as utilities or retail. SAP typically focused on best practice methodologies for driving its software processes, but more recently expanded into vertical markets. For instance, an invoice from the billing transaction of Sales & Distribution would pass through to accounting, where it will appear in accounts receivable and cost of goods sold. Įach module handled specific business tasks on its own, but was linked to the other modules where applicable. The most widely used modules were Financials and Controlling (FICO), Human Resources (HR), Materials Management (MM), Sales & Distribution (SD), and Production Planning (PP). SAP R/3 was arranged into distinct functional modules, covering the typical functions in a business organization.
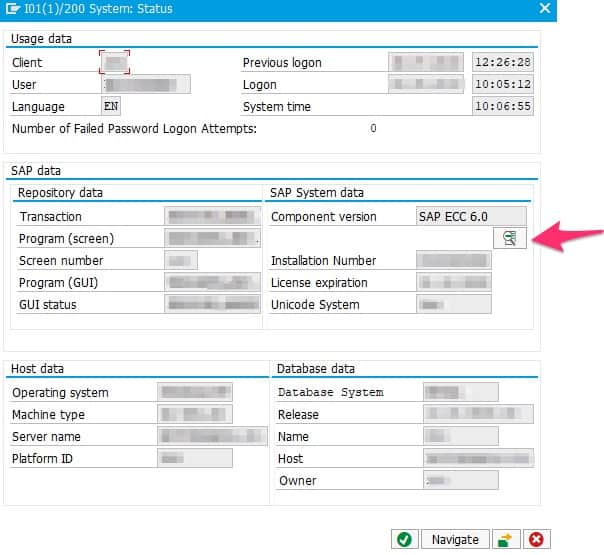
SAP enhancement package 8 for SAP ERP 6.0 (EHP8 FOR SAP ERP 6.0): 20 January 2016. SAP Fiori 1.0 for SAP ERP (UI FOR EHP7 FOR SAP ERP 6.0): 29 November 2013. SAP enhancement package 7 for SAP ERP 6.0 (EHP7 FOR SAP ERP 6.0): 13 August 2013. SAP enhancement package 6 for SAP ERP 6.0 (EHP6 FOR SAP ERP 6.0): 24 August 2011. SAP enhancement package 5 for SAP ERP 6.0 (EHP5 FOR SAP ERP 6.0): 12 July 2010.  SAP enhancement package 4 for SAP ERP 6.0 on SAP enhancement package for SAP NetWeaver 7.0 (EHP4 FOR SAP ERP 6.0 / NW7.01): 21 November 2008. SAP enhancement package 4 for SAP ERP 6.0 (EHP4 FOR SAP ERP 6.0): 21 November 2008. SAP enhancement package 3 for SAP ERP 6.0 (EHP3 FOR SAP ERP 6.0): 7 December 2007. SAP enhancement package 2 for SAP ERP 6.0 (EHP2 FOR SAP ERP 6.0): 27 July 2007. SAP enhancement package 1 for SAP ERP 6.0 (EHP1 FOR SAP ERP 6.0): 21 December 2006. SAP ERP Central Component (ECC) 6.0: 24 October 2005. SAP ERP Central Component (ECC) 5.0: 21 June 2004. SAP R/3 Enterprise Edition 4.6C (SAP R/3 4.6C): 3 April 2000. SAP R/3 Enterprise Edition 4.6B (SAP R/3 4.6B): 6 December 1999. SAP R/3 Enterprise Edition 4.0B (SAP R/3 4.0B): 6 April 1998. SAP R/3 Enterprise Edition 3.1l (SAP R/3 3.1I):. SAP R/3 Enterprise Edition 2.0B (SAP R/3 2.0B): July 1993. SAP R/3 Enterprise Edition 1.0 A: July 1992. The classic three-tier and database-agnostic architecture of R/3 is replaced with a two-tier architecture. S/4 has a single tenant architecture and is being built upon SAP's in-memory database technology stack (HANA) and will be available in a choice of in-cloud and on-premises deployment. The combined complexity of the Business Suite, along with newer in-cloud competitors, has in recent years led SAP to invest heavily in simplification and massively improved system response times, culminating in the announcement of the S/4 Simple Suite in February 2015. Finance module, HR module, Warehouse Management etc. SAP ECC contains different, but integrated, functionality within its "modules" e.g. SAP ECC is the core component within the SAP's Business Suite (a collection of applications including SAP CRM, SAP SCM and others, alongside the ECC component). The newest version of the product is SAP ECC 6.0 Enhancement Pack 8. SAP came to dominate the large business applications market. Various releases of the software were made through the 1990s.Ī newer version of the software, with revised technical architecture, was released in 2004, and renamed as SAP ERP Central Component (ECC). SAP R/3 was officially launched on 6 July 1992. This opened up SAP to a whole new customer base.
SAP enhancement package 4 for SAP ERP 6.0 on SAP enhancement package for SAP NetWeaver 7.0 (EHP4 FOR SAP ERP 6.0 / NW7.01): 21 November 2008. SAP enhancement package 4 for SAP ERP 6.0 (EHP4 FOR SAP ERP 6.0): 21 November 2008. SAP enhancement package 3 for SAP ERP 6.0 (EHP3 FOR SAP ERP 6.0): 7 December 2007. SAP enhancement package 2 for SAP ERP 6.0 (EHP2 FOR SAP ERP 6.0): 27 July 2007. SAP enhancement package 1 for SAP ERP 6.0 (EHP1 FOR SAP ERP 6.0): 21 December 2006. SAP ERP Central Component (ECC) 6.0: 24 October 2005. SAP ERP Central Component (ECC) 5.0: 21 June 2004. SAP R/3 Enterprise Edition 4.6C (SAP R/3 4.6C): 3 April 2000. SAP R/3 Enterprise Edition 4.6B (SAP R/3 4.6B): 6 December 1999. SAP R/3 Enterprise Edition 4.0B (SAP R/3 4.0B): 6 April 1998. SAP R/3 Enterprise Edition 3.1l (SAP R/3 3.1I):. SAP R/3 Enterprise Edition 2.0B (SAP R/3 2.0B): July 1993. SAP R/3 Enterprise Edition 1.0 A: July 1992. The classic three-tier and database-agnostic architecture of R/3 is replaced with a two-tier architecture. S/4 has a single tenant architecture and is being built upon SAP's in-memory database technology stack (HANA) and will be available in a choice of in-cloud and on-premises deployment. The combined complexity of the Business Suite, along with newer in-cloud competitors, has in recent years led SAP to invest heavily in simplification and massively improved system response times, culminating in the announcement of the S/4 Simple Suite in February 2015. Finance module, HR module, Warehouse Management etc. SAP ECC contains different, but integrated, functionality within its "modules" e.g. SAP ECC is the core component within the SAP's Business Suite (a collection of applications including SAP CRM, SAP SCM and others, alongside the ECC component). The newest version of the product is SAP ECC 6.0 Enhancement Pack 8. SAP came to dominate the large business applications market. Various releases of the software were made through the 1990s.Ī newer version of the software, with revised technical architecture, was released in 2004, and renamed as SAP ERP Central Component (ECC). SAP R/3 was officially launched on 6 July 1992. This opened up SAP to a whole new customer base. #Sap ecc stand for windows#
This new architecture is compatible with multiple platforms and operating systems, such as Microsoft Windows or UNIX. With the advent of distributed client–server computing, SAP SE brought out a client–server version of the software called SAP R/3 (the "R" was for "Real-time data processing" and "3" was for " 3-tier": 1) database, 2) application server, and 3) client (SAPgui)). It was particularly popular with large multinational European companies that required soft-real-time business applications, with built-in multi-currency and multi-language capabilities. SAP R/2 was a mainframe-based business application software suite that was very successful in the 1980s and early 1990s.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
